
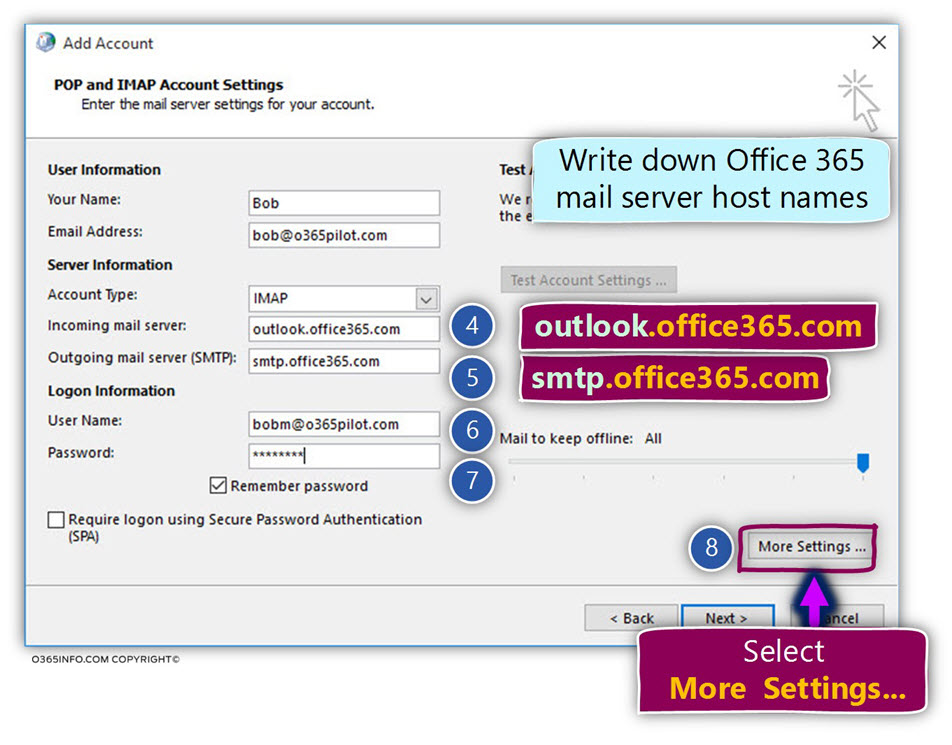
You want to set up DKIM keys for email originating out of a third-party domain, for example, if you use a third-party bulk mailer.You want to customize your CNAME records.You're going to set up DMARC too ( recommended).You have more than one custom domain in Microsoft 365.However, you should manually configure DKIM for your custom domain in the following circumstances: Microsoft-365's built-in DKIM configuration is sufficient coverage for most customers. If you don't set up DKIM for your custom domain, Microsoft 365 creates a private and public key pair, enables DKIM signing, and then configures the Microsoft 365 default policy for your custom domain. You can choose to do nothing about DKIM for your custom domain too.

DKIM verification helps the receiving servers confirm the mail is really coming from your domain and not someone spoofing your domain. The public key is published in the domain's DNS records, and receiving servers can use that key to decode the signature. In basic, a private key encrypts the header in a domain's outgoing email. Email systems that get email from your domain can use this digital signature to help verify whether incoming email is legitimate.
When you configure DKIM, you authorize your domain to associate, or sign, its name to an email message using cryptographic authentication. For more information about domains, see Domains FAQ.ĭKIM is one of the trio of Authentication methods (SPF, DKIM and DMARC) that help prevent attackers from sending messages that look like they come from your domain.ĭKIM lets you add a digital signature to outbound email messages in the message header. That means you don't need to do anything to set up DKIM for any initial domain names (for example, ). Microsoft 365 automatically sets up DKIM for its initial '' domains.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
